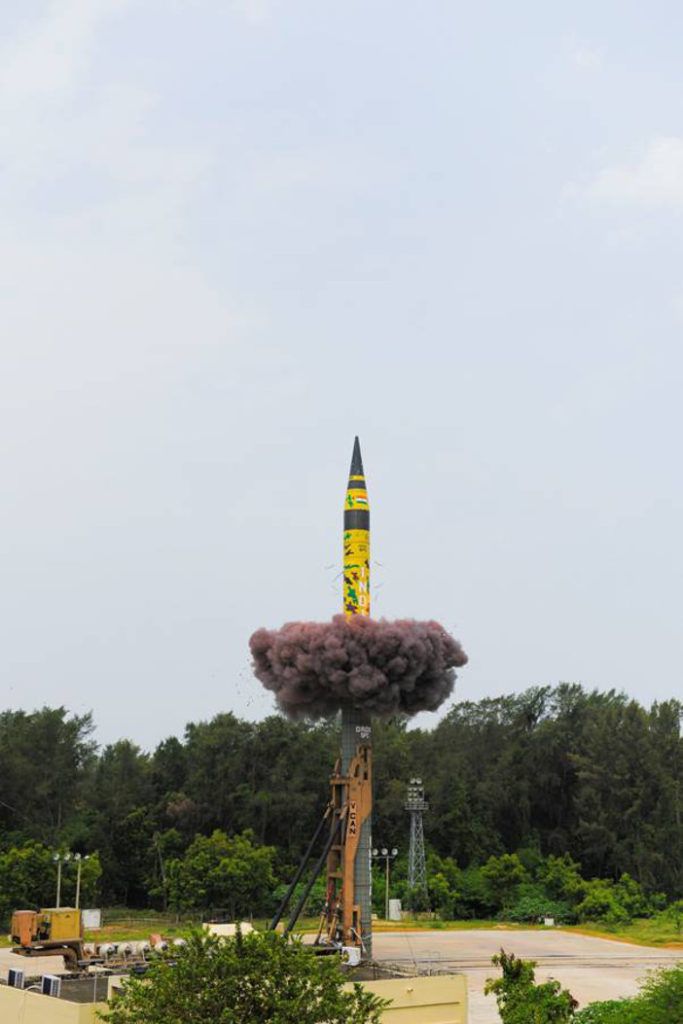
India’s Agni V, an indigenously developed, nuclear capable surface-to-surface ballistic mile, was successfully flight-tested during June.
After a successful launch, which took place at the integrated test range on Abdul Kalam Island, off the coast of the east Indian state Odisha, the intermediate-range missile flew 5,000km (3,100 miles) before hitting its target. The missile was successfully tracked by radar, electro-optical tracking stations and telemetry stations, said the Indian Government and “all mission objectives were achieved.”
This is the sixth test flight for India’s intercontinental ballistic missile, which was first flight-tested in April 2012. The Agni V’s range means it can reach potential targets in China.
The Agni V is a three stage solid fueled missile which uses composites throughout its design to reduce weight. The missile is launched by a mobile launcher.